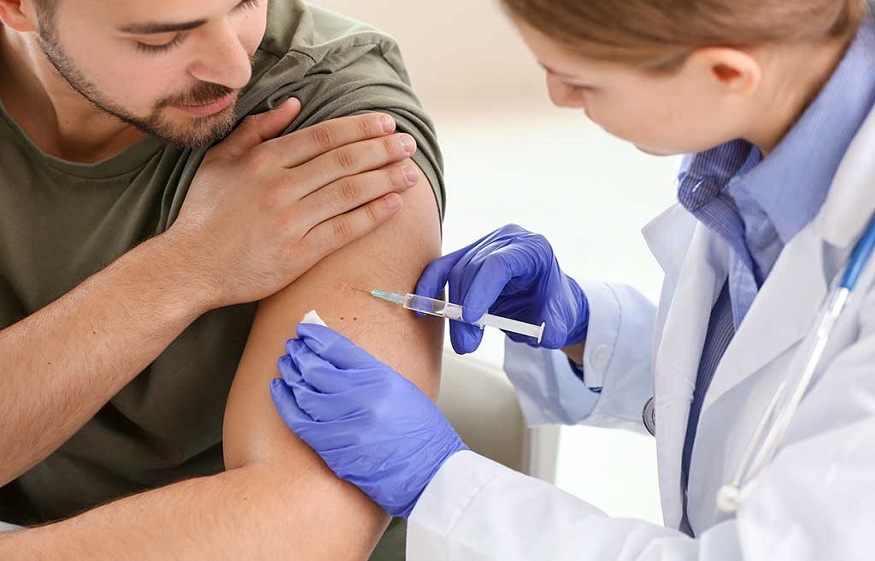
The Role of Flu Shots in Preventing Outbreaks of Influenza: An Overview of Herd Immunity
The influenza virus is a major public health concern, causing millions of illnesses and thousands of deaths worldwide each year. While many people may dismiss the flu as a minor inconvenience, it can be a serious illness, especially for young children, older adults, and those with weakened immune systems. One of the most effective ways to prevent outbreaks of influenza is through vaccination. In this article, we will explore the role of flu shots in preventing the spread of the flu, and how herd immunity plays a critical role in protecting those most vulnerable to the virus. We’ll also address common concerns like pain after flu shot and flu shot death, and explain why these risks are very rare.
What is a flu shot?
A flu shot, also known as a flu vaccine, is a vaccine that protects against the influenza virus. The flu shot is made up of inactivated viruses or pieces of viruses that stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies against the flu virus. These antibodies can protect against the flu virus if a person is exposed to it.
The flu shot is recommended for everyone over six months of age, but it is especially important for people at higher risk of complications from the flu, such as young children, pregnant women, older adults, and people with certain chronic medical conditions.
Pain After Flu Shot
It is common to experience mild side effects after receiving the flu shot, including soreness, redness, or swelling at the injection site, headache, fever, and muscle aches. These side effects are usually mild and go away on their own within a few days. However, some people may experience more severe side effects, such as an allergic reaction or Guillain-Barré syndrome, a rare but serious neurological disorder. It is important to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider before getting a flu shot.
Flu Shot Death
There have been rare cases of people dying after receiving the flu shot. However, these deaths are extremely rare and usually occur in people with underlying health conditions or in rare cases of severe allergic reactions. The benefits of getting a flu shot far outweigh the risks, and it is important to remember that the flu itself can lead to severe complications and death.
What is herd immunity?
Herd immunity, also known as community immunity, occurs when a large portion of a population becomes immune to a disease, either through vaccination or previous infection. When enough people are immune to a disease, it becomes difficult for the disease to spread from person to person, even to those who are not immune. This helps protect people who cannot be vaccinated or are at high risk of complications from the disease.
Herd immunity is particularly important for diseases like the flu, which can spread quickly and easily from person to person. The flu vaccine is a powerful tool in achieving herd immunity because it not only protects the person who receives the vaccine but also helps protect those around them.
How does the flu vaccine protect against the flu?
The flu vaccine works by stimulating the immune system to produce antibodies against the flu virus. These antibodies can recognize and fight off the flu virus if a person is exposed to it. The flu vaccine is updated each year to protect against the strains of the flu virus that are expected to be most common during the upcoming flu season.
The flu vaccine is not 100% effective, but even if a person who has been vaccinated gets the flu, the vaccine can help reduce the severity of the illness and prevent complications.
How does herd immunity work for the flu?
When enough people in a community are vaccinated against the flu, it becomes difficult for the flu virus to spread from person to person, even to those who are not vaccinated. This helps protect people who cannot be vaccinated, such as infants and people with certain medical conditions, and reduces the overall spread of the disease.
The concept of herd immunity is particularly important for protecting vulnerable populations, such as young children and older adults, who are at higher risk of complications from the flu. By reducing the overall spread of the disease, herd immunity can help prevent outbreaks of the flu and reduce the number of hospitalizations and deaths from the virus.
It is important to note that achieving herd immunity requires a high level of vaccination coverage in the population. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends a vaccination coverage rate of at least 70% to 90% to achieve herd immunity for the flu.
Conclusion
The flu can be a serious illness, especially for those who are most vulnerable to the virus. Herd immunity plays a critical role in preventing outbreaks of influenza, and flu shots are a key tool in achieving this protection. While some people may have concerns about side effects like pain after flu shot or flu shot death, it is important to understand that serious side effects are rare. Getting a flu shot is a safe and effective way to protect yourself and your community against the flu. By working together to achieve herd immunity, we can help to prevent the spread of influenza and keep our communities healthy.
If you or a loved one has experienced severe side effects from a flu shot or other vaccine, it is important to seek legal guidance. Visit Vaccine Law to learn more about your legal options and how to protect your rights.




